Google Unveils TranslateGemma: A New Era of Open Translation Models Built on Gemma 3 Architecture
Google has officially released TranslateGemma, a groundbreaking series of open translation models based on the Gemma 3 architecture. Available in 4B, 12B, and 27B parameter sizes, these models leverage advanced two-stage fine-tuning to deliver state-of-the-art performance across 55 languages. This article provides a comprehensive technical deep dive into the architecture, training methodology, and the transformative potential of running high-fidelity translation on edge devices.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Artificial Intelligence, the quest for a truly universal translator has been one of the field’s “Holy Grails” since its inception. While cloud-based APIs like Google Translate have served billions of users for over a decade, the paradigm is shifting. The demand for privacy-preserving, low-latency, and customizable translation solutions has driven a surge of interest in open-weight models that can run locally.
On January 15, 2026, Google marked a significant milestone in this journey with the release of TranslateGemma, a specialized suite of translation models built upon the powerful Gemma 3 architecture. This release is not merely an incremental update; it represents a fundamental rethinking of how translation models are trained, optimized, and deployed. By offering three distinct parameter sizes—4B, 12B, and 27B—Google is effectively democratizing access to state-of-the-art translation capabilities, enabling everything from real-time on-device translation on smartphones to research-grade linguistic analysis on consumer laptops.
This comprehensive analysis delves deep into the technical innovations behind TranslateGemma, exploring its unique training pipeline, the significance of its performance metrics, and the broader implications for the future of global communication.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic Model Sizing: The suite includes a 4B model optimized for mobile/edge devices, a 12B model for high-performance local development, and a 27B model for enterprise-grade cloud deployment.
- Architectural Excellence: Built on the cutting-edge Gemma 3 foundation, leveraging native multimodal capabilities without the need for separate vision encoders.
- Revolutionary Training Pipeline: Utilizes a novel “Two-Stage Fine-Tuning” process combining Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with high-quality synthetic data and Reinforcement Learning (RL) guided by advanced reward models.
- Next-Gen Evaluation Metrics: optimized using MetricX-QE and AutoMQM, moving beyond traditional BLEU scores to prioritize semantic nuance and human-like fluency.
- Unmatched Efficiency: The 12B model outperforms the larger 27B baseline, effectively halving the computational requirement for top-tier translation.
- Global Reach: Native support for 55 core languages with experimental training on nearly 500 languages, aiming to preserve and revitalize endangered dialects.
1. The Architecture: Gemma 3 Meets Specialized Fine-Tuning
To understand the significance of TranslateGemma, one must first appreciate its foundation. The Gemma 3 architecture represents Google’s latest advancement in open models, characterized by improved parameter efficiency and native multimodal understanding. Unlike previous generations where translation was often treated as just another downstream task for a general-purpose Large Language Model (LLM), TranslateGemma treats translation as a primary, specialized discipline.
1.1 The “Jack of All Trades” Problem
General-purpose LLMs are notoriously good at many things but often struggle with the specific constraints of high-fidelity translation. They may hallucinate content, miss subtle cultural nuances, or default to a “translationese” style that sounds unnatural to native speakers. Google’s solution to this was a rigorous, specialized post-training process.
1.2 Two-Stage Fine-Tuning: The Secret Sauce
The technical brilliance of TranslateGemma lies in its “Two-Stage Fine-Tuning” recipe, which meticulously sculpts the raw intelligence of the Gemma 3 base model into a disciplined translator.
Stage 1: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Synthetic Brilliance
The first stage involves Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). However, Google didn’t just rely on existing parallel corpora (which can be noisy or low-quality). Instead, they leveraged their most powerful proprietary model, Gemini, to generate vast amounts of high-quality synthetic translation data. This “Teacher-Student” distillation approach allows the smaller TranslateGemma models to absorb the complex reasoning and linguistic capabilities of the massive Gemini model. By mixing this pristine synthetic data with gold-standard human-translated datasets, Google created a training corpus of unprecedented quality. This ensures that the model learns not just how to translate, but how to translate well, capturing idioms, tone, and register.
Stage 2: Reinforcement Learning (RL) with Advanced Reward Models
SFT gets the model 90% of the way there, but to bridge the “last mile” gap to human-level parity, Google employed Reinforcement Learning (RL). In the context of translation, RL is challenging because defining a “reward” is difficult—there are many valid ways to translate a sentence. To solve this, Google utilized two cutting-edge reward models:
- MetricX-QE (Quality Estimation): This is a reference-free metric. Unlike BLEU, which simply compares the output to a reference translation, MetricX-QE analyzes the source text and the translated output to predict a quality score directly. It acts like a rigorous human editor, flagging translations that “feel” wrong even if they match keywords.
- AutoMQM (Multidimensional Quality Metrics): This system automates the MQM framework, which is the industry standard for identifying specific errors (like mistranslation, omission, or grammatical errors).
By using these sophisticated judges to guide the RL process, TranslateGemma was trained to maximize semantic quality and fluency rather than just statistical overlap.
2. Performance Analysis: Doing More with Less
One of the most compelling aspects of the TranslateGemma release is the efficiency gains demonstrated in the technical report. In the world of AI, “bigger is better” has been the prevailing dogma. TranslateGemma challenges this narrative.
2.1 The 12B “Sweet Spot”
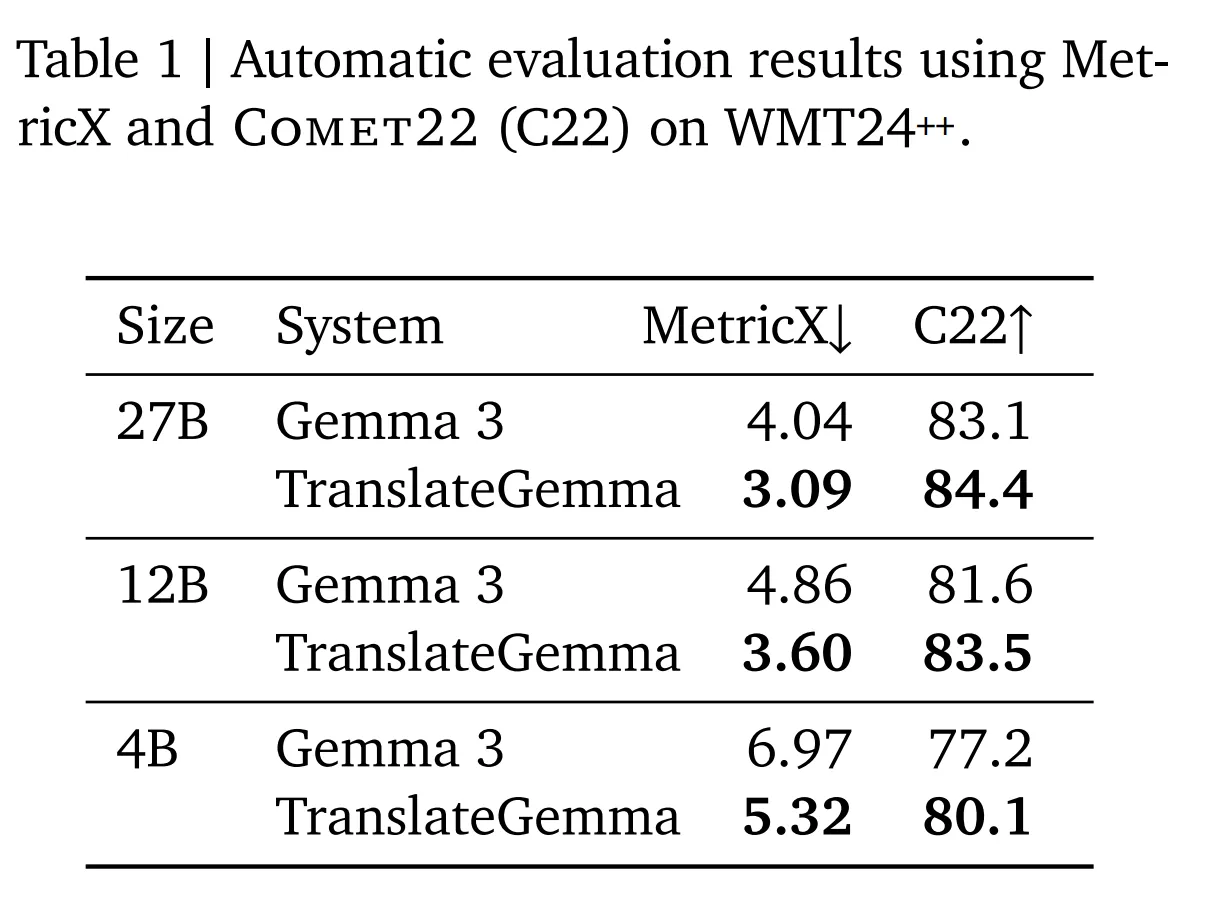
The 12B parameter model is arguably the star of the show. According to Google’s internal benchmarks using WMT24++ (a rigorous test suite covering high, medium, and low-resource languages), the TranslateGemma 12B model produces translations of a higher quality than the Gemma 3 27B baseline model. This is a massive engineering achievement. It means that developers and researchers can achieve state-of-the-art results using half the VRAM and compute power previously required. For a local deployment scenario, this is the difference between needing a dedicated server and running comfortably on a high-end consumer laptop (like a MacBook Pro or a PC with an RTX 4090).
2.2 The 4B Model: A Mobile Powerhouse
Perhaps even more impressive is the 4B model. Designed specifically for edge devices, this model’s performance rivals that of the 12B baseline. This has profound implications for mobile applications:
- Offline Capability: Users can have high-quality translation without an internet connection, crucial for travelers or aid workers in remote areas.
- Privacy: Sensitive data (like business documents or personal chats) never needs to leave the device.
- Latency: On-device inference eliminates network round-trips, enabling near-instantaneous speech-to-speech translation.
3. Native Multimodality: Seeing the World in Any Language
TranslateGemma inherits the native multimodal capabilities of the Gemma 3 architecture. This is a significant departure from traditional pipelines that use “Cascaded Systems” (e.g., Image -> OCR -> Text -> Translation). In a cascaded system, errors propagate. If the OCR misreads a character, the translator has no way to recover. TranslateGemma, however, processes visual tokens and text tokens in a shared semantic space. This means the model can “see” the context of the text. For example, if it sees the word “Bank” on a building in an image, it knows to translate it as a financial institution rather than the side of a river, based on the visual cues of the building itself. This holistic understanding leads to significantly better translations for real-world scenarios like translating menus, street signs, or technical manuals.
4. Linguistic Diversity: The “Long Tail” of Language
While the model officially launches with support for 55 core languages (covering the vast majority of the world’s internet population), Google’s ambition extends much further. The technical report mentions experimental training on nearly 500 languages. This focus on “low-resource” languages is critical. Many of the world’s 7,000+ languages are in danger of digital extinction because there isn’t enough data to train traditional models. By using transfer learning—where the model applies what it knows about the structure of Spanish to a related but resource-scarce language like Galician—TranslateGemma helps bridge the digital divide. This capability provides academic researchers with a powerful foundation for preserving and studying endangered languages.
5. Deployment Scenarios: Choosing the Right Tool
Google has clearly segmented the three models to address specific market needs:
5.1 The 4B Model: The “Edge” Warrior
- Ideal For: Android/iOS apps, IoT devices, Smart Glasses.
- Use Case: A pair of AR glasses that translates a restaurant menu in real-time as you look at it. The 4B model is small enough to run on the device’s NPU, ensuring battery efficiency and instant feedback.
5.2 The 12B Model: The “Pro” Workhorse
- Ideal For: Desktop software, Local R&D, Content Creation.
- Use Case: A game developer localizing their indie game into 10 languages. They can run the 12B model on their development machine to generate first-pass translations for all dialogue, significantly reducing localization costs.
5.3 The 27B Model: The “Server” Titan
- Ideal For: Enterprise APIs, Large-scale Document Processing.
- Use Case: A multinational legal firm processing millions of pages of discovery documents. They can deploy the 27B model on a private cloud (using H100s or TPUs) to ensure maximum accuracy and data sovereignty.
6. The Future of Open Translation
The release of TranslateGemma signals a maturing of the open-source AI ecosystem. We are moving away from “one model to rule them all” toward specialized, highly optimized models that excel at specific tasks. For developers, this is an invitation to innovate. The barriers to entry for creating sophisticated translation applications have never been lower. Whether it’s building a real-time translation bot for a Discord server or creating a privacy-focused document translator for medical professionals, the tools are now freely available.
Furthermore, the “open weights” nature of TranslateGemma allows the community to take ownership. We can expect to see fine-tuned variants of TranslateGemma appearing on Hugging Face shortly—versions specialized for medical terminology, legal jargon, or even slang and internet-speak.
Conclusion
TranslateGemma is more than just a set of model weights; it is a testament to the power of specialized architecture and rigorous training methodologies. By successfully compressing state-of-the-art performance into accessible 4B and 12B packages, Google has effectively uncorked the potential for high-quality translation to be ubiquitous, private, and instantaneous.
As we move forward into 2026, the distinction between “what a phone can do” and “what a supercomputer can do” continues to blur. TranslateGemma is a clear harbinger of this future, where language barriers are dismantled not by massive data centers, but by the intelligent chips in our pockets.
Disclaimer: This article is based on the official announcement and technical details available as of January 16, 2026. Model performance metrics and availability are subject to change as the technology evolves. Please refer to the official Google DeepMind technical report and the Hugging Face model cards for the most up-to-date information.